Orthopaedic Surgery is a specialized branch of medicine focused on diagnosing, treating, and surgically managing conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves. Orthopaedic surgeons are medical professionals who perform surgeries and provide treatments to address injuries, deformities, and diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Key Aspects of Orthopaedic Surgery:
Goal of Orthopaedic Surgery:
- The primary goal of orthopaedic surgery is to restore the function and mobility of the musculoskeletal system. This may involve the repair of bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, or muscles, as well as correcting deformities or addressing chronic conditions.
- Pain relief, improved movement, and restoration of strength are common goals of orthopaedic treatments.
Common Conditions Treated in Orthopaedic Surgery: Orthopaedic surgeons treat a wide range of conditions, including:
- Fractures: Breaks or cracks in bones due to trauma or injury. Treatment can involve setting the bone, using pins or plates, or, in some cases, surgery to realign bones.
- Arthritis: A degenerative disease affecting the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. The most common types treated are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Joint replacement surgeries (like hip or knee replacements) are often performed.
- Ligament and Tendon Injuries: Injuries such as ACL tears, rotator cuff tears, and Achilles tendon ruptures may require surgical intervention for repair.
- Joint Deformities: Conditions like scoliosis, hip dysplasia, and clubfoot require correction through surgery or other interventions.
- Spinal Disorders: Conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or scoliosis may require surgical treatment to decompress nerves or correct misalignments.
- Sports Injuries: Injuries sustained during physical activity, including tears, fractures, and dislocations, which may require surgical intervention to repair the affected areas.
- Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors: Benign or malignant tumors affecting bones and soft tissues may require removal or reconstruction surgeries.
- Osteoporosis: A condition in which bones become brittle and prone to fractures. Orthopaedic surgeons may treat fractures associated with osteoporosis and manage preventative strategies.
Types of Orthopaedic Surgeries: Orthopaedic surgery includes both minimally invasive and traditional open surgical procedures, depending on the condition being treated:
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure where small incisions are made, and a camera is used to view the joint. It is commonly used for conditions like torn cartilage, ligament injuries, and joint problems in the knee, shoulder, or hip.
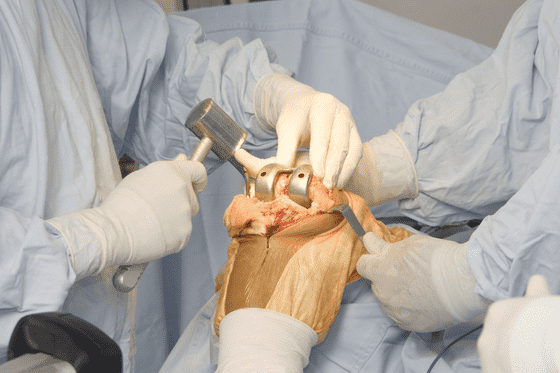
- Joint Replacement Surgery (Arthroplasty): This involves replacing a damaged joint with a prosthesis. Common joint replacement surgeries include knee replacement, hip replacement, and shoulder replacement. The goal is to relieve pain and improve function.
- Fracture Repair: Surgical treatment of broken bones may involve realigning bone fragments and stabilizing the fracture using plates, screws, pins, or rods.
- Spinal Surgery: Procedures like laminectomy, discectomy, or spinal fusion are performed to treat conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or scoliosis.
- Tendon Repair Surgery: This involves repairing torn or ruptured tendons, such as the rotator cuff in the shoulder or the Achilles tendon in the ankle.
- Ligament Reconstruction: For torn ligaments, such as the ACL in the knee, a surgical procedure may involve reconstructing the torn ligament using grafts.
- Bone Tumor Removal: Surgical procedures may be required to remove benign or malignant tumors affecting bones or soft tissues.
Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery:
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Many orthopaedic surgeries can now be performed using smaller incisions and advanced technology, such as arthroscopy or robotic-assisted surgery. This typically leads to quicker recovery, less pain, and reduced risk of infection.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Some complex procedures, such as joint replacements, are now performed with the assistance of robotic technology, providing enhanced precision and better outcomes.
- Open Surgery: In more complex cases, traditional open surgery may still be required, which involves larger incisions to provide direct access to the affected area.
Orthopaedic Surgery Procedures:
- Knee and Hip Replacement (Arthroplasty): This procedure involves replacing a damaged joint (usually due to arthritis) with a prosthetic. The surgeon removes the damaged portion of the bone and joint, replacing it with artificial components.
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction: The ACL is a ligament in the knee that can be torn due to injury. Surgery typically involves reconstructing the ligament using a graft from another tendon or ligament.
- Rotator Cuff Repair: The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons in the shoulder. Tears can be repaired surgically using minimally invasive techniques or open surgery.
- Spinal Fusion: This surgery is performed to treat conditions such as degenerative disc disease or scoliosis by fusing two or more vertebrae together, providing stability and alleviating pain.
- Fracture Fixation: Broken bones may be realigned and stabilized using plates, screws, rods, or pins. The type of fixation used depends on the fracture’s location and severity.
- Tendon and Ligament Repair: This involves repairing damaged tendons and ligaments, such as the Achilles tendon or the ACL in the knee, often with grafts or sutures.
Recovery After Orthopaedic Surgery:
- Postoperative Care: Recovery after orthopaedic surgery depends on the type of procedure performed. Patients may require medications for pain management, physical therapy, or assistive devices such as crutches or braces to aid in the healing process.
- Physical Therapy: After surgery, physical therapy is often recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion. This is particularly important after joint replacements, tendon or ligament repairs, or fractures.
- Rest and Rehabilitation: Full recovery may take weeks to months, depending on the severity of the surgery. Patients may be required to follow a rehabilitation program designed to help them regain function and mobility.
Risks and Complications: As with any surgery, orthopaedic procedures carry some risks, including:
- Infection: A risk of infection can occur after surgery, particularly in joint replacements or open surgeries.
- Blood Clots: There is a risk of blood clots forming, especially after hip or knee surgeries. Patients are often prescribed blood thinners or encouraged to move regularly to prevent this.
- Nerve Injury: Some surgeries may involve a risk of nerve damage, particularly in spinal or joint surgeries.
- Implant Failure: In joint replacements, there is a risk of the implant loosening, wearing out, or becoming dislocated over time.
- Persistent Pain: In some cases, pain may persist after surgery, requiring further treatment or adjustments.
When Is Orthopaedic Surgery Needed?: Orthopaedic surgery may be recommended if:
- Conservative treatments (like physical therapy, medications, or injections) have not provided relief.
- There is a severe injury (e.g., broken bones, torn ligaments, or dislocations).
- A condition is affecting mobility and quality of life, such as severe arthritis or degenerative joint disease.
- There is a need for correction of deformities (e.g., scoliosis or hip dysplasia).
- Infection or tumors affecting bones or joints require surgical removal.
- Pain management from chronic conditions (like osteoarthritis) cannot be achieved without surgery.
Advancements in Orthopaedic Surgery:
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic systems help orthopaedic surgeons perform procedures with greater precision, improving outcomes and reducing recovery times.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Advances in arthroscopy and other minimally invasive procedures allow for faster recovery times, smaller scars, and reduced complications.
- Biologics and Stem Cell Therapy: Research in biologics, including stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP), aims to promote healing and tissue regeneration in joints, ligaments, and tendons.
- 3D Imaging and Printing: 3D imaging allows for better pre-surgical planning, while 3D printing is used for customized implants and surgical tools.



